Banafsha Tahir
Banafsha Tahir
In South Asian countries like India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, transgender people often face tough challenges. They’re usually seen as less and face a lot of discrimination. In Pakistan, many transgender individuals are not accepted at home and join Hijra communities, where they live under a guru’s guidance. They struggle not just in these communities but also in wider society, dealing with things like social, economic, and political unfairness. Often, they’re treated poorly outside their communities, looked down upon, and left out of welcoming places. These issues make it hard for them to fully be a part of the larger society.
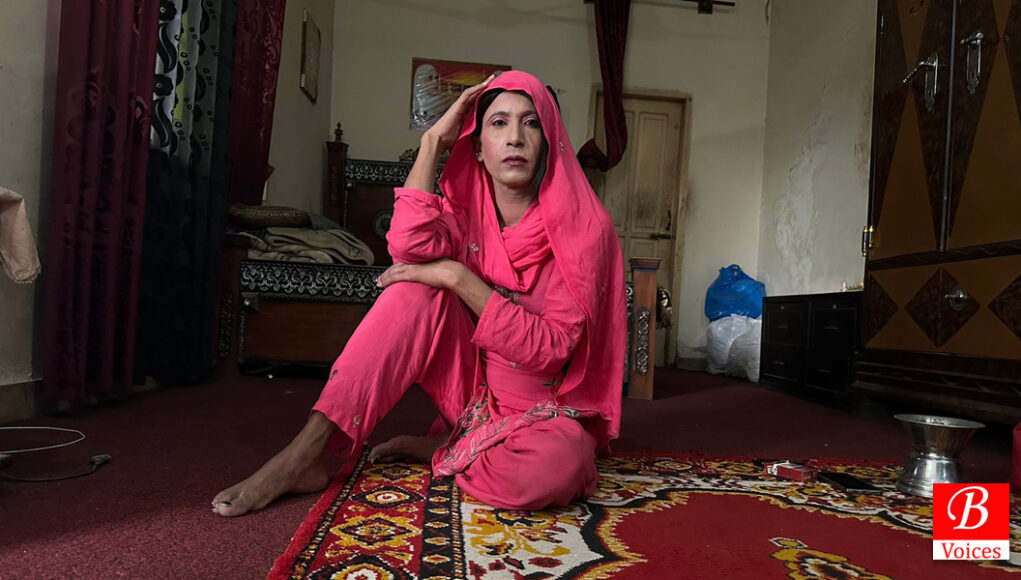
Meet Lubna, a brave soul from Multan Chichawatni, now living in Islamabad’s G-12 sector. Coming from a humble background and orphaned, she worked as a laborer in homes. As time passed, Lubna embraced her identity as a transgender person and left her village. In Islamabad, she found a supportive transgender community and a guru who showed her how to live her truth. Now 35, Lubna is a revered leader and mentor for other transgender individuals. She looks after her community, providing support and engaging in social initiatives. Lubna organizes food distributions, not just during Ramadan, but beyond. She also sets up toy stalls and income opportunities for her community. Recently, she encouraged them to join a new school for transgenders opened by the army on May 29, 2023, where she was a guest speaker. Lubna’s journey is a tale of courage, resilience, and kindness.
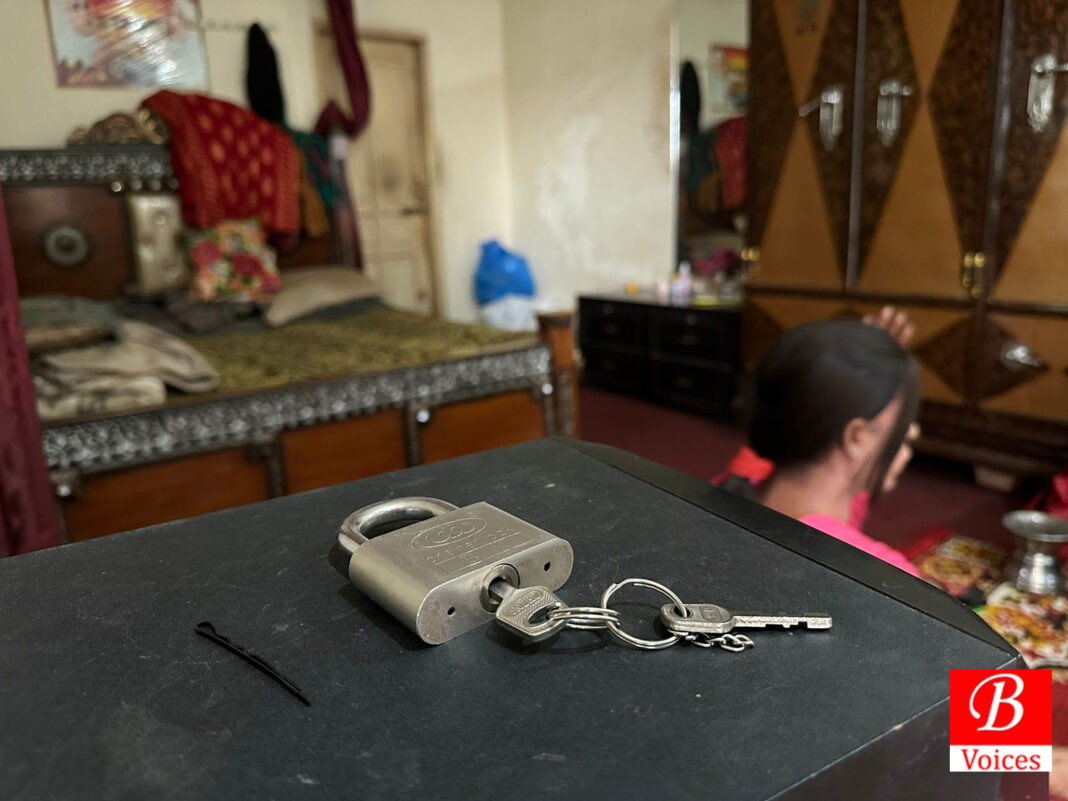


Lubna’s story is a powerful example of bravery, resilience, and kindness. Unfortunately, despite their courage, transgender individuals still face a lot of fear for their safety because of how society treats them. To protect themselves, they often have strict rules about keeping their doors locked at night and waiting until morning to open them, no matter how serious the situation may be. This is because they have experienced terrible things, like what happened to Lubna’s transgender friend. Her friend was tricked by a group of people pretending to need help, but instead, they entered her house and hurt her in awful ways. They were very cruel and even shaved her hair off to humiliate her even more. After the incident, Lubna was involved more in activity to find a way to make people aware of the unjust with the trans community and started working with NGOs, Social rights activists, and government organizations.

UN Human Rights
The UN Human Rights has recorded instances of discrimination and stigma against transgender people across various domains such as healthcare facilities, educational institutions, employment opportunities, housing, and bathroom access. Furthermore, there is also a lack of recognition of their gender identity. Consequently, the UN Human Rights has provided recommendations to governments on how to improve the protection of the rights of transgender individuals.
1: “Urging for Comprehensive Anti-Discrimination Laws: Protecting the Rights of Transgender Individuals”
2: Legally recognize the gender identity of trans people in official documents through a simple administrative process based on self-identification without abusive requirements such as forced medical diagnosis, sterilization, treatment, or divorce.
3: Ensure effective recording, reporting, investigation, and prosecution of acts of violence and torture against trans people and remedy for victims.
4: Train police officers, healthcare workers, teachers, judges, prison officials, immigration officers, and other officials on respect and equal treatment of trans people
5: Ensure access to health services including gender-affirming procedures for trans people without stigma, discrimination, or abusive requirements.
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act 2018
In Pakistan, transgender people have faced discrimination and marginalization for not conforming to traditional gender norms. They are vulnerable to violence and persecution, leading to begging and prostitution for survival. In 2018, Pakistan enacted the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act to address these issues, but its impact and implementation remain uncertain. More efforts are needed to protect transgender rights and ensure their effective inclusion in society.
The Khawajasira community, also known as transgender women, has historically struggled for their rights. The Supreme Court’s ruling in the case of Muhammad Aslam Khaki v. SSP Operations Rawalpindi highlighted the need for provincial governments to protect their fundamental rights. This decision led to additional options in the “sex” category on official documents to recognize gender diversity. The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill was also enacted in 2017, showing progress in legislating for transgender rights. However, there are still shortcomings in the Act, including the need for a comprehensive definition, exclusion of certain groups, and inadequate protections for sexual orientation and gender expression. Reforms should focus on new legislation, penalizing hate crimes, inheritance rights, education, and institutions, and raising awareness to ensure transgender rights are fully protected.

Transgender Rights and Urban Poverty
Transgender individuals in Pakistan face significant barriers to education and employment, resulting in a higher risk of poverty, particularly in urban areas. Discrimination and stigma limit their job prospects, pushing them into low-income sectors where they are vulnerable to exploitation. Limited access to education perpetuates the cycle of poverty, as discrimination and bullying in schools often lead to high dropout rates. This denies transgender individuals the skills needed for better employment opportunities. The lack of social support systems further exacerbates their situation, hindering access to healthcare, housing, and necessities. To address this, comprehensive policies are required, including inclusive education, vocational training, and employment initiatives. Targeted social protection programs can also provide healthcare, housing, and financial support, improving their overall well-being. By recognizing and addressing the link between transgender rights and urban poverty, Pakistan can work towards an inclusive society that empowers all its citizens, irrespective of gender identity

Conclusion
In addition to the positive steps taken towards the rights and inclusion of transgender individuals in Pakistan, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and areas that still require attention. Despite the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, violence against transgender communities remains a significant concern. Transgender individuals continue to face high levels of discrimination, harassment, and physical abuse, often resulting in severe consequences such as injury, trauma, or even loss of life. Addressing this issue requires concerted efforts from the government, law enforcement agencies, and society as a whole to create a safer environment and ensure justice for victims. Furthermore, the violation of transgender rights in various aspects of life is an ongoing issue. Many transgender individuals face barriers in accessing education, healthcare, employment, and housing opportunities. Discrimination in these areas further marginalizes transgender communities, limiting their chances for personal growth, economic stability, and social integration. Policymakers must work towards eliminating these barriers and promoting inclusive policies that ensure equal rights and opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their gender identity.
Another challenge is the lack of knowledge and awareness among the general population regarding transgender issues. Prejudices, stereotypes, and misconceptions often contribute to the discrimination and marginalization faced by transgender individuals. Educational initiatives and awareness campaigns are necessary to foster understanding, empathy, and acceptance within society. By promoting accurate information, challenging stereotypes, and encouraging dialogue, Pakistan can foster a culture of inclusion and respect for transgender individuals. To address these issues effectively, ongoing collaboration between government bodies, civil society organizations, and transgender advocacy groups is essential. By working together, they can develop comprehensive strategies that prioritize the protection of transgender rights, promote social acceptance, and provide support systems for transgender individuals. Moreover, it is crucial to engage religious leaders, community leaders, and influential figures in promoting acceptance and countering discriminatory beliefs, as their support can significantly impact societal attitudes.
In conclusion, while Pakistan has made significant progress in recognizing and protecting the rights of transgender individuals, there are still challenges to overcome. By addressing violence, promoting awareness, and eliminating systemic barriers, Pakistan can build a future where transgender individuals are celebrated, respected, and treated with dignity and equality. Continued efforts and a collective commitment from all sectors of society are vital to achieving this vision.
The writer is an MS Journalism student, who writes inspiring articles about marginalized communities, highlighting their stories and perspectives. She aims to amplify voices that deserve recognition and bring attention to often-overlooked narratives.
Disclaimer: Views expressed in this article are those of the writer and Balochistan Voices does not necessarily agree with them.
Share your comments!